Expected to become an important tool for non-invasive diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal diseases in the future
Recently, the team led by Cui Daxiang from Shanghai Jiao Tong University published their latest research findings in 《Biosensors and Bioelectronics》. They have successfully developed an intelligent magnetic controlled wireless powered near-infrared fluorescent capsule endoscopy (NIFCE). With the significant breakthrough of this capsule endoscopy technology, gastrointestinal diseases such as early gastric cancer, colon cancer, colitis, etc. will be diagnosed early. With its efficient and accurate detection capabilities, NIFCE is expected to become an important tool for non-invasive diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases in the future.
In the field of modern medical diagnosis, although traditional wired endoscopic techniques are widely used in clinical practice, they still have certain limitations. For example, the invasive nature of the operation can cause physical and mental discomfort to the patient. Therefore, the development of new diagnostic methods has always been a common concern for the medical industry and patients.
With the advancement of technology and the development of artificial intelligence, non-invasive intelligent capsule endoscopy technology has gradually emerged, becoming a solution that subverts tradition and provides patients with a new and more comfortable examination technology. However, there are still limitations in the accuracy and energy supply of the existing capsule endoscopy technology for lesion diagnosis. These technologies limit the wider application of capsule endoscopy, especially in terms of its ability to accurately diagnose and treat critical lesions in the early stages.
The new near-infrared fluorescent capsule endoscope developed by Cui Daxiang’s team can not only capture conventional white light images for identifying lesions with significant morphological changes, but most importantly, when used in conjunction with near-infrared fluorescent probes, it can specifically “light up” specific lesion tissues, while normal tissues do not produce fluorescence. This feature allows doctors to clearly distinguish between diseased tissue and normal tissue, greatly improving the accuracy of early diagnosis. It enables accurate imaging diagnosis of lesions that were previously unable to be diagnosed by conventional capsule endoscopes without significant morphological changes, as well as lesions hidden below the mucosa.
In addition, this study also solved the problems of long-term energy supply and precise motion control of capsule endoscopes, and developed the industry’s first prototype system that can simultaneously provide wireless energy and wireless magnetic control for capsule endoscopes. It passed authoritative third-party testing (CJBG202310081, CJBG02310082, CJBG02310083).
Under the leadership of Professor Cui Daxiang, the team not only validated the feasibility of NIFCE in the laboratory, but also demonstrated its successful and specific detection of gastric cancer in live experiments, demonstrating its enormous potential in clinical applications.
Professor Cui Daxiang pointed out that the success of this study not only opens up a new path for the development of capsule endoscopy technology, but also provides enormous potential for the treatment and application of capsule endoscopy in gastrointestinal diseases.
It is understood that the team led by Cui Daxiang has for the first time integrated targeted nano probes for diagnosis and treatment of gastric cancer, achieving precise targeted imaging diagnosis and local chemotherapy, magnetothermal therapy, photodynamic therapy, in situ vaccine treatment, activating the immune system, achieving precise treatment of in situ lesions and micro metastatic lesions, and eliminating the potential for recurrence and metastasis. Combining microneedle technology to achieve biopsy of local lesions; By combining drug storage and delivery modules, therapeutic drugs can be directly delivered to the affected area, achieving precise treatment. For example, delivering small intestine fluid from healthy children to the transverse colon can effectively treat intestinal obstruction. We have developed a radial expansion capsule robot (Tribology Letters 2024; 72:22), which can effectively treat intestinal obstruction.
At present, the team led by Cui Daxiang is collaborating with the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University to organize the recruitment of volunteers and conduct clinical trials. The goal is to accelerate the clinical application of intelligent magnetic controlled wireless powered capsule endoscopy, serving the national health strategy.
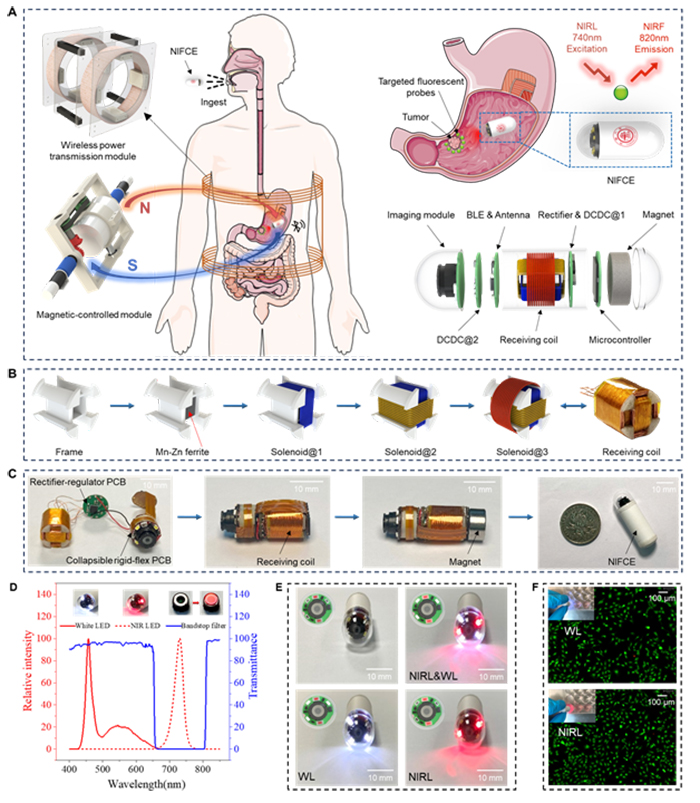 Overview of operation and design of near-infrared fluorescence imaging capsule endoscopes
Overview of operation and design of near-infrared fluorescence imaging capsule endoscopes
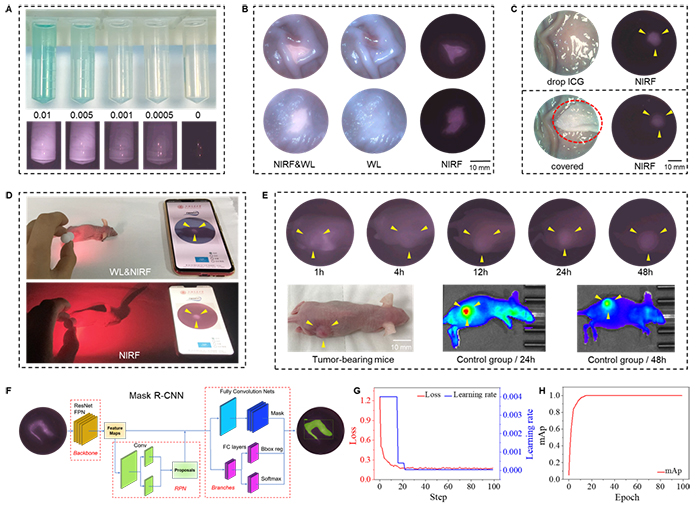 Accurate imaging of submucosal lesions in the gastrointestinal tract using near-infrared capsule endoscopy
Accurate imaging of submucosal lesions in the gastrointestinal tract using near-infrared capsule endoscopy
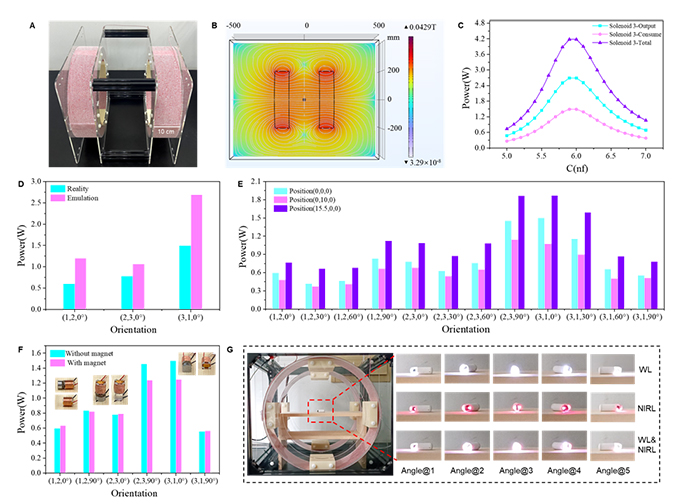 Wireless power supply mode for capsule endoscopy
Wireless power supply mode for capsule endoscopy
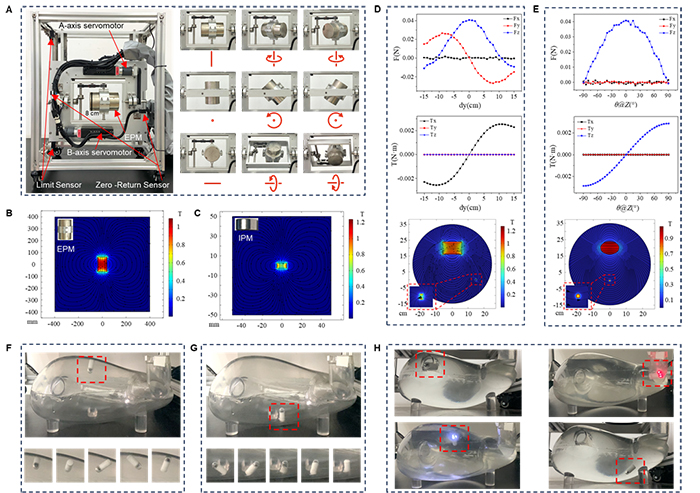 The Mode of Extracorporeal Magnetic Control System Regulating Capsule Endoscopy in the Gastrointestinal Tract
The Mode of Extracorporeal Magnetic Control System Regulating Capsule Endoscopy in the Gastrointestinal Tract
 社科在线
社科在线




